HYDROGEN & CAES™
INTEGRATED PROJECTS
We pioneer, adopt, and develop innovative low-carbon green energy technologies which integrate CAES and hydrogen projects with many other green energy technologies.
We configure entirely bespoke projects comprising many elements including renewable energy generation, CAES (electricity storage), electrolysis, hydrogen production and storage, fuel/chemical synthesis, and other end-uses of both renewable electricity and green hydrogen including iron and steel making, desalination and water treatment.
In these ways and more, Storelectric’s technologies can help to drive the green energy transition.
The Future of Energy
We expect future energy networks to be like today’s networks with two major elements: hydrogen and electricity; today, they are methane and electricity.
With investment, methane grids can be converted to hydrogen grids. Much recent grid investment globally has been hydrogen compatible. Of course, electricity is needed to make hydrogen, and hydrogen in turn is needed to make synthetic fuels, but what is transmitted along networks will mainly be these two. As with today’s gas and electricity grids, CAES™ and hydrogen projects are mutually complementary; they compete little with each other and some applications use both.
Hydrogen will feature primarily through:
- The gas grid
- Industrial processes (e.g. iron and steel making)
- Heating
- Transportation
- Synthetic fuels
- Catalysing other processes such as CAES.
So hydrogen solutions must be at the same scale as the gas plants and equipment that they replace.
HYDROGEN PRODUCTION WITH CAES
FOR OPTIMUM EFFICIENCY
HYDROGEN STORAGE SOLUTIONS
UNDER PRESSURE
An average lorry-sized tank, carrying hydrogen at 20bar pressure, can carry only 75kg of hydrogen. Therefore massive-scale storage is required. Our proprietary CAES system utilises salt caverns to store air pressurised with energy from renewable sources (which is later released to regenerate electricity). With some adjustments through higher-grade materials in drill strings, wellheads and pipework, adjacent caverns can be utilised to store hydrogen – typically storing 10,000–200,000 times as much as a tanker.
Hydrogen is typically produced at 30–300 bar pressure; our pressure control system allows us to maintain the same pressure for storage, minimising the energy consumed in storage.
ELETROLYSIS NEEDS
A STABLE ENVIRONMENT
Electrolysis (and fuel/chemical synthesis) operates far less efficiently – and with a much shorter plant life – when powered intermittently, requiring 2-6X more electrolysers to achieve the same output.
By integrating CAES™ in a renewables & hydrogen project, we deliver near-baseload energy to the electrolysers, as well as high-value services to the electricity grid, very cost-effectively.
A STAND ALONE
HYDROGEN TECHNOLOGY
Salt cavern storage is the only technology currently available that can store hydrogen safely and cheaply in massive bulk.
HYDROGEN & CAES
BETTER TOGETHER
Storelectric’s CAES™ (electricity storage) and hydrogen technologies are ideal jointly as inputs to many other processes that need both to be delivered concurrently. These include:
- Renewable generation of almost any type, including mixed, at large scale;
- Fuel and chemical synthesis, e.g. ammonia (NH3) and methanol (CH3OH), which are used as fuels and feedstock in other processes;
- Iron and steel making, where hydrogen replaces coal for both heat and chemical reduction processes;
- Synthesis of other hydrocarbons;
- Other industrial and chemical processes.
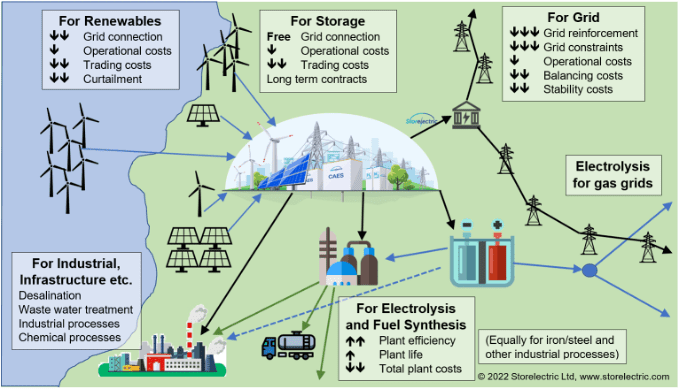
Integrating CAES™ and hydrogen projects: the more that are integrated, the more efficient and cost effective the whole development.


